. . .

Projecten & activiteiten
-
 ALMOSTYOU
ALMOSTYOU
gastvrijheid
-
 Autohotel
Autohotel
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Bikes to Borrow
Bikes to Borrow
geschiedenis
-
 Blauwe Huis Cinema
Blauwe Huis Cinema
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Bloemen voor IJburg
Bloemen voor IJburg
instante stedelijkheid
-
Blue Meetings
gastvrijheid
-
 Blue Print
Blue Print
geschiedenis
-
 Boekenkas
Boekenkas
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Brief van Marcel Möring
Brief van Marcel Möring
geschiedenis
-
 Chattheater
Chattheater
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Chill-ROOM
Chill-ROOM
instante stedelijkheid
-
 City Telling IJburg
City Telling IJburg
geschiedenis
-
 Creatief op IJburg
Creatief op IJburg
geschiedenis
-
 Debat 'Kunst van het samenleven'
Debat 'Kunst van het samenleven'
gastvrijheid
-
 Do you wanna work it?
Do you wanna work it?
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Faculty of Invisibility
Faculty of Invisibility
gastvrijheid
-
 Frida
Frida
gastvrijheid
-
 Galerie Evolution de l'art
Galerie Evolution de l'art
geschiedenis
-
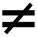 Gast≠vrij
Gast≠vrij
gastvrijheid
-
 Geluidswandeling IJburg
Geluidswandeling IJburg
geschiedenis
-
 Hollow Land
Hollow Land
geschiedenis
-
 Huisstijl
Huisstijl
geschiedenis
-
 Identiteitbouwer
Identiteitbouwer
geschiedenis
-
 IJBOARD
IJBOARD
geschiedenis
-
 IJboot
IJboot
instante stedelijkheid
-
 IJbuild
IJbuild
geschiedenis
-
 Kunstboom
Kunstboom
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Leesjeblauw
Leesjeblauw
instante stedelijkheid
-
 M2M Radio
M2M Radio
gastvrijheid
-
Motel Out of the Blue
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Parade der Stedelijkheid
Parade der Stedelijkheid
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Periscoop
Periscoop
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Proeflokaal
Proeflokaal
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Project Johan Siebers
Project Johan Siebers
gastvrijheid
-
 Publieke moestuin
Publieke moestuin
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Pump Up The Blue
Pump Up The Blue
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Rondleiding door de stilte
Rondleiding door de stilte
geschiedenis
-
 Schaduwcurator
Schaduwcurator
gastvrijheid
-
 Schoolmaken
Schoolmaken
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Sing for your supper
Sing for your supper
gastvrijheid
-
 Socially Yours
Socially Yours
gastvrijheid
-
 Spreekuur
Spreekuur
instante stedelijkheid
-
 Stedelijk in de stad
Stedelijk in de stad
gastvrijheid
-
 Think Tank
Think Tank
geschiedenis
-
 Van pionieren tot wonen
Van pionieren tot wonen
geschiedenis
-
 ZIJ-Power
ZIJ-Power
geschiedenis
-
 ZZP krant
ZZP krant
geschiedenis
Bewoners & bewerkers
-
Bart Janssen
Landschapsarchitect (Nederland, woont en werkt in Arnhem)
-
Cesare Pietroiusti
Kunstenaar (Italie, woont en werkt in Rome)
-
Cheikh Sakho
Schilder (Senegal, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Daniela Paes Leao
Kunstenaar en filmmaker (Portugal, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Dennis Kaspori
Architect (Nederland, woont en werkt in Rotterdam)
-
Dennis Straat
Stadsdeelwethouder Zeeburg
-
Elke Krasny
Curator (Oostenrijk, werkt en woont in Wenen)
-
Eveline de Munck Mortier
Beeldend kunstenaar (Nederland)
-
Floris van Heijnsbergen
Beeldend kunstenaar (Nederland)
-
Frida
Beeldend kunstenaar
-
Herve Paraponaris
Beeldend kunstenaar (Frankrijk, woont en werkt in Rotterdam)
-
Het Blauwe Huis
-
Howard Chan
Kunstenaar/directeur The AiR Association Limited (China, woont en werkt in Hong Kong)
-
Igor Dobrocic
Theatermaker/programmadirecteur ECF (Servië, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Igor Roovers
Programma manager Projectbureau IJburg
-
IJburg TV
www.ijburgtv.nl
-
Inga Zimprich
Kunstenaar and kunsttheoretica (Duitsland, woont en werkt in Maastricht / Ukraine)
-
Ingrid Meus
Kunstenaar (Nederland, woont en werkt in Den Haag)
-
Jeanne van Heeswijk
Beeldend kunstenaar (Nederland, woont en werkt in Rotterdam)
-
Jo van der Spek
Radiomaker (Nederland, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Johan Bakker
Bewoners IJburg, initiatiefnemer van De Boekenkas
-
Johan Siebers
Filosoof (Nederland, woont en werkt in Londen)
-
Joost Grootens
Kunstenaar en vormgever (Nederland, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
M7red (Mauricio Corbalan + Pio Torroja)
Architecten (Argentinië, wonen en werken in Buenos Aires)
-
Marcel Möring
Schrijver (Nederland, woont en werkt in Rotterdam)
-
Marianne Maasland
Kunsthistoricus (Nederland, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Marthe van Eerdt
Bewoner IJburg, Initiatiefnemer kinderbibliotheek Leesjeblauw
-
Nicoline Koek
Kunsthistorica, ondernemer en initiatiefnemer Bloemen voor IJburg
-
Nuno Sacramento
Schaduwcurator (Portugal, woont en werkt in Lissabon)
-
Orgacom
Kunstenaars en cultureel intermediair (Nederland, wonen en werken in Amsterdam en Istanbul)
-
Peter van Keulen
Bewoner IJburg, initiatiefnemer van IJboot
-
Pilot Publishing (Ella Gibbs + Amy Plant)
Kunstenaars (Engeland, wonen en werken in Londen)
-
Roé Cerpac
Beeldend kunstenaar (Israël, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Rudy Luijters
Beeldend kunstenaar (Nederland, woont en werkt in Brussel)
-
Sarah van Sonsbeeck
Kunstenaar (Nederland, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Silvia Russel
Beeldend kunstenaar (Nederland, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Silvia Russel
Beeldend kunstenaar (Nederland, woont en werkt in Amsterdam)
-
Sonia Boyce
Kunstenaar (Engeland, woont en werkt in Londen)
-
soundtrackcity
Soundtrackcity Amsterdam
-
Stedelijk Museum
Stedelijk Museum Amsterdam
-
Tere Recarens
Kunstenaar (Spanje, woont en werkt in Berlijn)
-
Transparadiso (Barbara Holub + Paul Rajakovics)
Kunstenaar & stedenbouwkundige/architect (Oostenrijk, wonen en werken in Wenen)
-
Usha Mahabiersing
Bewoonster IJburg, initiatiefnemer van de Blauwe Huis Cinema
-
Yane Calovski
Kunstenaar en schrijver (Macedonië, woont en werkt in Skopje)
sluiten 
sluiten 
Nieuwsarchief
Januari 2010
December 2009
November 2009
Oktober 2009
September 2009
Augustus 2009
Juli 2009
Juni 2009
Mei 2009
April 2009
Maart 2009
- Reuze periscoop geeft IJburg zijn uitzicht terug
- Teken de petitie Uitzicht op!
- Woensdag 25 maart 13.00-17.00: Kunstbus Noordje op Wielen
- Zaterdag 28 maart: De kunst van het samenleven
- Het Nieuwe Gezin. Een verslag van Anique Weve
- Verslag; The (un)making of IJburg
- Zaterdag 14 maart 15.00: Een 'maakbare' samenleving
- Hands-on Utopia
- Uitzicht op! Een nieuwe kijk op IJburg
- Zaterdag 7 maart 15.00: Ideaal Wonen
- Beeldverslag filmavond Women Only 12 februari
Februari 2009
Januari 2009
December 2008
Oktober 2008
September 2008
Augustus 2008
Juli 2008
Juni 2008
Mei 2008
April 2008
Maart 2008
Februari 2008
Januari 2008
December 2007
November 2007
Oktober 2007
September 2007
- Film Legrain en Beauvent
- Speciale last minute actie voor IJburgers
- Programma Autohotel
- Gezocht: medewerkers Autohotel
- Filmpje: Autohotel door Olga Russel
- Nieuwsbrief 19
- Radio Ruisriet M2M 28 september
- Filmpje: Identiteitbouwer door Daniela Paes Leao
- Filmpje Blauwe Huis Cinema door Jessie Vreden
- Filmpje Autohotel door Bright TV
- 3 oktober: Peter Faber vertelt geheimzinnige verhalen
- 22 september: Blok 35 Party
- Radio Ruisriet M2M 21 september
- Proeflokaal
- Moeders’ Mooiste: IJburg in tekeningen
- Nieuwsbrief 18
- Just another idea....
- Radio Ruisriet M2M 14 september
- 8 september: 'Scene's from the Balcony'
- Nieuwsbrief 17
- Radio Ruisriet M2M 7 september
- 1 september: extra kamer voor Het Blauwe Huis
- Presentatie 'Atlas of Suggestion' 1-9 September
Augustus 2007
Juli 2007
Juni 2007
Mei 2007
April 2007
Februari 2007
November 2006
September 2006
Mei 2006
April 2006
Maart 2006
September 2005
Mei 2005
April 2005
Maart 2005
Juni 2004
Mei 2004

sluiten 
A project by Jeanne van Heeswijk & Hervé Paraponaris
Background
In 1996, Amsterdam City Council decided to proceed with the development of IJburg, a residential district as an alternative to the city centre and surrounding areas. These residential areas are being created on a cluster of manmade islands, and the project is set for completion in 2012. The district will then provide 18,000 dwellings for 45,000 residents. These dwellings are primarily being constructed in a block layout, each composed of a mix of owner-occupied dwellings and social-sector rental housing, in the proportion 80:20. All the dwellings are situated around a communal courtyard or garden. IJburg must also provide employment opportunities for 12,000 people. Besides housing, schools and shops, plans include construction of sports facilities, restaurants, a beach and a cemetery. Typical of a new habitat like IJburg is that the entire project is devised in the conference room and on the drawing board. In this process, nothing is left to chance.
Though IJburg is not a ‘problem’ area, it is lacking something extremely important, namely a history – a social and human history, stories, life and a beating heart. Each of these qualities and elements must grow, and cannot be planned on the drawing board or built by a contractor. It has been demonstrated that these qualities are decisive for an area’s identity as well as for its inhabitants and users. They are therefore of crucial importance. In contrast to old city quarters, which can look back upon a rich history, in IJburg it is only possible to look ahead. However, the first pioneers are already starting to leave the area, in search of a new challenge, while for other people it is attractive that the district is at last starting to take shape. History can be written as you go along, but then it must be recognized as such, documented and developed further.
Themes
According to urban planning expert Bart Wissink, criticism of the planning methodology used for IJburg, among other places, has become extremely stark. Such rigorously regulated, zoned expansion districts are frequently cited as examples of where a predetermined spatial intervention is also meant to lead to the residents gaining a sense of community. However, he wonders, does it really work like this? It has already been a long time since people organized themselves on this scale; their lives extend far beyond the borders of the neighbourhood and even the city, and activities are also conducted on a diversity of scales. The attribution of an unambiguous identity to a particular place is, moreover, at odds with the character of the space, which is open to multiple interpretations. But on a larger scale as well, the impossibility of ‘makeable’ society (or, in this case, ‘plannable’ society) is becoming increasingly evident. Urbanity is often hard to detect in the majority of expansion districts of the last decade. They are areas that are based wholly on the doctrine of segregation. The division of functional domains such as living and working, the separation of infrastructure, the separation of income groups (social-sector rental housing versus owner-occupied homes), and so on and so forth. This doctrine of segregation stems from the craving for control. This doctrine is also the reason why no form of urbanity can ever develop in these areas. That is because urbanity is founded on encounter: interpersonal encounter, the encounter of cultures, ideas, and so on. For example, the encounter of different ideas sparks new ideas. Urban qualities, a beating heart, shared history, social interaction and a sense of community are, indeed, all qualities that must grow and evolve; they cannot be planned on the drawing board or be built by a contractor.
This also applies for the Haveneiland (‘Harbour Island’), with its ‘Castellum’ (also known as 'Block 35') designed by TKA (Teun Koolhaas Associates, now Atelier DUTCH). This block is also composed of a mix of owner-occupied dwellings and social-sector rental housing. All the units in 'Block 35' are situated around a communal courtyard, which has a cobalt blue townhouse in the middle. On the initiative of the artist Jeanne van Heeswijk, the 'Blauwe Huis' (‘Blue House’), which was already a bone of contention because of its position (something like an observation post or lookout within the block), will not be put up for sale for a period of at least four years. The point of this is to establish it as a house for culture and a place for research into the development and evolution of history and experimental communities. It is a spot that cannot be regulated within a living environment that has been planned down to the last millimeter, a place for exchange and dialogue.
Because of its position on IJburg (an artificially created island) as part of the newly built residential area under development there, the Blue House is the ideal platform for research into how such a district takes shape and the way in which people go about using, appropriating and changing the public space. Block 35 is one of the first sections being developed on IJburg. The Blue House can therefore follow the development of IJburg and the development of this new community up close. This combination of location and a particular moment in time, coupled with the opportunity to be a temporary co-inhabitant of IJburg, offers the Blue House’s residents an ideal platform for studying, acting on and co-designing the public space on IJburg.
Aims and Objectives
In the history of art, the desire for a ‘house for the arts’ is nothing unusual. On 9 September 1888, Vincent van Gogh wrote about his ‘Yellow House’ in Arles in a letter to his colleague Gauguin. In this letter, Van Gogh expressed his desire to establish a house where he could offer hospitality to fellow artists with whom he wished to work intensively and exchange ideas. A place for living and working, as well as for presentation and debate, would be accommodated under a single roof. He created such a place in what would later become known as the Yellow House. There have, indeed, been more places like this. For example, Frida Kahlo and Diego Rivera lived at the renowned and notorious 'Casa Azul' (‘Blue House’) in Mexico in the period around 1940. Discussions that arose there and the artistic output did not simply have an influence on the city (via the medium of Diego’s murals) but also, thanks to guests like Leon Trotsky, even had an impact on world history. In turn, the Blue House can become a base from which IJburg, in its early years as a new society, can be scrutinized critically, and not only because of the prominent place within the block but particularly because of the imagination-sparking associations with its historical predecessors. It provides a platform for research into experimental communities and the development of a (future) history.
Over a four-year period, artists, architects, thinkers, writers and scholars of various nationalities are being invited to live and work in the Blue House for six-month residencies. These residents have been given the assignment of actively entering into a dialogue with one another, with their co-inhabitants in IJburg, and with the public. The aim is to establish links between the world within (their world) and outside (IJburg in development and the rest of the world), and thus become co-authors of IJburg’s genesis and evolutionary history, which also includes the cultural history of a community. The residents of the Blue House will interpret and translate the evolution of an identity, or indeed the search for it, in all kinds of different ways, simultaneously recording and documenting it for the future. By conducting research, producing works of art, films and publications, and holding presentations and other activities, a new infrastructure will be created in and around the house. An infrastructure, like a network, in which information is continuously exchanged about the evolving urban space and in which its problems will be rendered visible, too. The Blue House will therefore serve as an impulse for the urban dynamic by intervening locally with projects that could be seen as a form of ‘instant urbanity’. These are projects that make it possible to cut through the doctrine of segregation and attempt to make the public space into a shared space without this requiring large-scale urban interventions.
The Blue House functions like a catalyst for an accelerated formulation of history in IJburg. By describing and simultaneously intervening in everyday life in this area, the Blue House facilitates the acceleration and intensification of the process of developing a cultural history. The studies and projects to be initiated from the Blue House exist outside the tradition of standard cultural historiography. They do not constitute a cultural monograph or a ‘retroactive manifesto’, but are an experimental form of historiography in which documentation and production are interwoven in a unique way.
sluiten 
The Blue House
A project by Jeanne van Heeswijk & Hervé Paraponaris
Background
In 1996, Amsterdam City Council decided to proceed with the development of IJburg, a residential district as an alternative to the city centre and surrounding areas. These residential areas are being created on a cluster of manmade islands, and the project is set for completion in 2012. The district will then provide 18,000 dwellings for 45,000 residents. These dwellings are primarily being constructed in a block layout, each composed of a mix of owner-occupied dwellings and social-sector rental housing, in the proportion 80:20. All the dwellings are situated around a communal courtyard or garden. IJburg must also provide employment opportunities for 12,000 people. Besides housing, schools and shops, plans include construction of sports facilities, restaurants, a beach and a cemetery. Typical of a new habitat like IJburg is that the entire project is devised in the conference room and on the drawing board. In this process, nothing is left to chance.
Though IJburg is not a ‘problem’ area, it is lacking something extremely important, namely a history – a social and human history, stories, life and a beating heart. Each of these qualities and elements must grow, and cannot be planned on the drawing board or built by a contractor. It has been demonstrated that these qualities are decisive for an area’s identity as well as for its inhabitants and users. They are therefore of crucial importance. In contrast to old city quarters, which can look back upon a rich history, in IJburg it is only possible to look ahead. However, the first pioneers are already starting to leave the area, in search of a new challenge, while for other people it is attractive that the district is at last starting to take shape. History can be written as you go along, but then it must be recognized as such, documented and developed further.
Themes
According to urban planning expert Bart Wissink, criticism of the planning methodology used for IJburg, among other places, has become extremely stark. Such rigorously regulated, zoned expansion districts are frequently cited as examples of where a predetermined spatial intervention is also meant to lead to the residents gaining a sense of community. However, he wonders, does it really work like this? It has already been a long time since people organized themselves on this scale; their lives extend far beyond the borders of the neighbourhood and even the city, and activities are also conducted on a diversity of scales. The attribution of an unambiguous identity to a particular place is, moreover, at odds with the character of the space, which is open to multiple interpretations. But on a larger scale as well, the impossibility of ‘makeable’ society (or, in this case, ‘plannable’ society) is becoming increasingly evident. Urbanity is often hard to detect in the majority of expansion districts of the last decade. They are areas that are based wholly on the doctrine of segregation. The division of functional domains such as living and working, the separation of infrastructure, the separation of income groups (social-sector rental housing versus owner-occupied homes), and so on and so forth. This doctrine of segregation stems from the craving for control. This doctrine is also the reason why no form of urbanity can ever develop in these areas. That is because urbanity is founded on encounter: interpersonal encounter, the encounter of cultures, ideas, and so on. For example, the encounter of different ideas sparks new ideas. Urban qualities, a beating heart, shared history, social interaction and a sense of community are, indeed, all qualities that must grow and evolve; they cannot be planned on the drawing board or be built by a contractor.
This also applies for the Haveneiland (‘Harbour Island’), with its ‘Castellum’ (also known as 'Block 35') designed by TKA (Teun Koolhaas Associates, now Atelier DUTCH). This block is also composed of a mix of owner-occupied dwellings and social-sector rental housing. All the units in 'Block 35' are situated around a communal courtyard, which has a cobalt blue townhouse in the middle. On the initiative of the artist Jeanne van Heeswijk, the 'Blauwe Huis' (‘Blue House’), which was already a bone of contention because of its position (something like an observation post or lookout within the block), will not be put up for sale for a period of at least four years. The point of this is to establish it as a house for culture and a place for research into the development and evolution of history and experimental communities. It is a spot that cannot be regulated within a living environment that has been planned down to the last millimeter, a place for exchange and dialogue.
Because of its position on IJburg (an artificially created island) as part of the newly built residential area under development there, the Blue House is the ideal platform for research into how such a district takes shape and the way in which people go about using, appropriating and changing the public space. Block 35 is one of the first sections being developed on IJburg. The Blue House can therefore follow the development of IJburg and the development of this new community up close. This combination of location and a particular moment in time, coupled with the opportunity to be a temporary co-inhabitant of IJburg, offers the Blue House’s residents an ideal platform for studying, acting on and co-designing the public space on IJburg.
Aims and Objectives
In the history of art, the desire for a ‘house for the arts’ is nothing unusual. On 9 September 1888, Vincent van Gogh wrote about his ‘Yellow House’ in Arles in a letter to his colleague Gauguin. In this letter, Van Gogh expressed his desire to establish a house where he could offer hospitality to fellow artists with whom he wished to work intensively and exchange ideas. A place for living and working, as well as for presentation and debate, would be accommodated under a single roof. He created such a place in what would later become known as the Yellow House. There have, indeed, been more places like this. For example, Frida Kahlo and Diego Rivera lived at the renowned and notorious 'Casa Azul' (‘Blue House’) in Mexico in the period around 1940. Discussions that arose there and the artistic output did not simply have an influence on the city (via the medium of Diego’s murals) but also, thanks to guests like Leon Trotsky, even had an impact on world history. In turn, the Blue House can become a base from which IJburg, in its early years as a new society, can be scrutinized critically, and not only because of the prominent place within the block but particularly because of the imagination-sparking associations with its historical predecessors. It provides a platform for research into experimental communities and the development of a (future) history.
Over a four-year period, artists, architects, thinkers, writers and scholars of various nationalities are being invited to live and work in the Blue House for six-month residencies. These residents have been given the assignment of actively entering into a dialogue with one another, with their co-inhabitants in IJburg, and with the public. The aim is to establish links between the world within (their world) and outside (IJburg in development and the rest of the world), and thus become co-authors of IJburg’s genesis and evolutionary history, which also includes the cultural history of a community. The residents of the Blue House will interpret and translate the evolution of an identity, or indeed the search for it, in all kinds of different ways, simultaneously recording and documenting it for the future. By conducting research, producing works of art, films and publications, and holding presentations and other activities, a new infrastructure will be created in and around the house. An infrastructure, like a network, in which information is continuously exchanged about the evolving urban space and in which its problems will be rendered visible, too. The Blue House will therefore serve as an impulse for the urban dynamic by intervening locally with projects that could be seen as a form of ‘instant urbanity’. These are projects that make it possible to cut through the doctrine of segregation and attempt to make the public space into a shared space without this requiring large-scale urban interventions.
The Blue House functions like a catalyst for an accelerated formulation of history in IJburg. By describing and simultaneously intervening in everyday life in this area, the Blue House facilitates the acceleration and intensification of the process of developing a cultural history. The studies and projects to be initiated from the Blue House exist outside the tradition of standard cultural historiography. They do not constitute a cultural monograph or a ‘retroactive manifesto’, but are an experimental form of historiography in which documentation and production are interwoven in a unique way.



 Ga naar boven…
Ga naar boven…
 lees verder
lees verder